Geography
Introduction
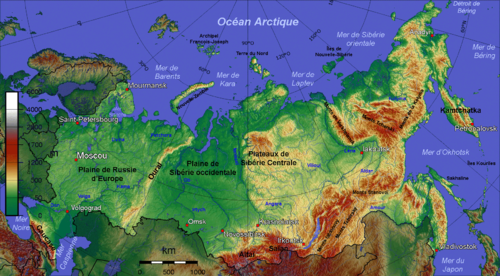
Russia is the most vast country of the world in front of Canada. She(it) occupies the North of Asia and is her(it) of Europe - for respectively 74,7 % and 25,3 % of her(its) territory. She(it) is separated from the American continent by the Bering Strait. His(her,its) total surface is a little more than 17 million km ², that is 11 % of lands appeared from the planet. His(her,its) capital Moscow is on the West, far from the geographical center of the country. The distances are gigantic: 150 ° of latitude, 9 time zones, 9000 km from west to east, 3000 km from north to south. Several days by train are needed to cross the country and the transport is expensive.
Situation
The Russian Federation occupies two continents: the European part(party) extends on the West mounts Ural, the Asian part(party) in the East. Russia possesses several maritime facades: the biggest, on the Arctic ocean in the North, is taken by the ice floe more than half than year. The Pacific Ocean lines is him(her,it): the oriental coast is very cut (peninsula tchouktche, peninsula of Kamchatka, gulf of Chelikhov) and look onto the Bering Sea, the Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan; the South Seas are Caspian Sea ( an inland sea) and the Black Sea. Finally, Russia has access to the Baltic Sea on the West where is the port(bearing) of Saint-Petersburg.
Relief
Mountain ranges do not represent a constraint important for transport because they occupy the margins of the Russian territory. Ural is the only mountain of meridian orientation and its passage is made easy by collars(passes) of low(weak) height. However, mountains cover near the third(third party) of the Russian territory and have generally low(weak) densities, except in certain sectors of the Caucasus and Ural.
The West of Russia is established(constituted) by a plain spread(widened) with low hills on the West by Ural. Central Siberia is a vast tray(plateau) crossed(gone through) by big rivers which flow(sink) northward. The Southern regions present a mountainous aspect .L' is from Russia belongs to the belt of fire(light) of the Pacific. Volcanoes dominate the peninsula of Kamchatka: the main summit of this region is Klioutchevskoï (4 835 meters).
Main summits
Elbrus 5 642 meters. It is the peak of Europe.
Klioutchevskoï 4 835 meters. It is the highest summit of the Asian part(party) of Russia
Mount Béloukha 4 506 meters. It is the peak of the Altai.
Hydrography
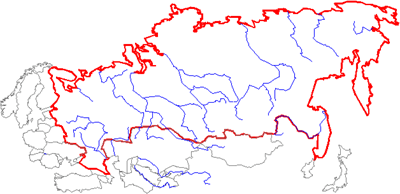
Main rivers:
Don
The Volga
The Ob (5410 km, 2,99 million km ²)
The Yenisei (5940 km, 2,58 million km ²)
The Lena (4337 km, 2,49 million km ²)
The Love (4440 km, 1,85 million km ²)
Kolyma
Main islands
In the Arctic ocean
François - Joseph's Earth
Novaya Zemlya (or piece of news-Earth(short story-Earth))
Severnaya Zemlya
Kolgouïev
Severnaya Zemlya
Piece of news-Siberia(Short story-Siberia)
Wrangel
Islands of the Commander
In the Pacific Ocean
The Kuril Islands
Sakhalin
Siberia is rich in raw materials: fossil fuels, ores and precious metals. But deposits(fields) are parfoistrès taken away from the inhabited regions. From 1930s, the USSR resolved this problem by creating of the heavy industry east of Ural. The light industries being rather concentrated in the urban zones.
From a geostrategic point of view, Siberia thus defines itself as the central gas, oil, gold-bearing and diamondiferous reservoir of Russia. Indeed, the majority of the potential of Russian production of these raw materials are concentrated in this region. For example, approximately 90 % of the production of natural gas results from the region of Tioumen and, in particular, from the autonomous district of Yamalo-Nenets, in the Big North, where are situated the huge deposits(fields) of Ourengoï (10 000 billion cubic meters) and of Iambourg (5 000 billion cubic meters). In the same region, the deposits(fields) of the peninsula of Yamal offer reserves in gas exceeding(irritating) 10 000 billion cubic meters. Other more modest zones of production are implanted in the Republic of Komi and in Yakutia. The last one conceals important deposits(fields) of diamonds, among the most important for the world.
The development of the business connections with Asia overloaded the railroad and road network of Siberia. More and more transport are made by waterway, in particular on the Love.
